#GERD#Hyperglycemia#LIPH#Fasting#HyaluronicAcid #Collagen #LiverGallbladderCleanse #Hemp #Stress #BrainAge #Drugs #EndocrineDisruptiors #Hypertension#Microplastics #WaterSmarts #ToxicChemicals #LiverHealth #MilkThrisle #Magnesium #LiverCleanse #MedicinalMushroomsForAtheleticPerformance #BrainBoostingMedicinalMushrooms #RoyalColloids #CalciumDGlucarate #ProteinMalfunction #MedicinalMushrooms #JapaneseLongevitySecret #PlantarFasciitis #BlackCuminTheBlackGold #ThroatThyroidEsophagusLarynx#BasicBiohacks#SkinHealth#VariousLipids #Radiation #LungHealth #Sinkholes #Praying #HepatitisC #ImmuneBoostingFoods #ImmuneBoostingSupplements #ImmuneBoostingBiohacks #BetaGlucans #BetaGlucanKids #Phytoplankton
Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive compound in the cannabis family and the only active compound in the hemp plant.
In 2004, has been found that some cannabinoids, specifically cannabidiol or CBD derived from the hemp plant alters genes that produce a compound known as VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor). This compound helps grow new blood vessels in cancer cells. When cancer cells begin to grow large, they need to start creating their own blood vessels. In other words CBD cuts off the tumor’s blood supply and cause cancer cells to commit suicide, e.g death by starvation.
This self-destruction is a form of what scientists called “programmed cell death”.
Programmed cell death occurs in two ways
- apoptosis
- autophagy.
Both apoptosis and autophagy are normal for cells. When a cell becomes too old or damaged, the body uses these mechanisms to eliminate the rogue cell. Unfortunately, cancer cells do not self-destruct. Rather, they continue to grow and grow, creating life-threatening tumors. Here comes the cannabinoids that are causing cancer cells to “auto-digest themselves”, or undergo autophagy. Cannabidiol CBD activates a signaling pathway that involves autophagy, which would be like the self-digestion of the cells. So, when CBD binds to tumor cells, it triggers a cell-signaling mechanism. 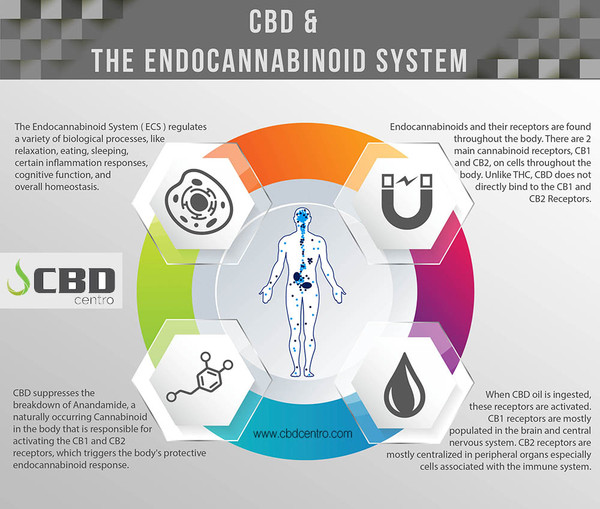
Cannabidiol (CBD) affects multiple tumoral features and molecular pathways, and induces cancerous cell death. Furthermore, cannabidiol (CBD) is causing a decreased expression of various proteins involved in the spread of the tumor. Yet again, this result was dependent on the dosage administered. CBD has a tendency to down-regulate pro-survival signaling pathways in each of the glioma cells as well.
Cannabidiol (CBD) is a source of phytocannabinoid, largely due to the compound’s lack of psychoactivity or THC that actually makes it universal tumor cells inhibitor. The lack of THC in the hemp plant provide efficiency with zero neuro or mobility side effects
Our body has thousands of cannabinoids receptors, and CBD is known to fit like a key/connector into network of existing connectors.
The Endocannabinoid system exist to receive cannabinoids
While it may be difficult to believe, cbd kills cancer cells. A wealth of recent research has found that cannabinoids, the active compounds in cannabis, prevent cancer from spreading, growing, and even cause tumor cells to die. But, how is all of this possible? We’ll tell you.
1. Anti-proliferative
One problem with cancer cells is that they don’t stop growing. Once a malignant tumor begins, cancer cells continue to divide and conquer. New cancer cells are continuously being made. The cells then rapidly spread to other tissues in the body. This process of growing and spreading is proliferation.
Here’s how cannabis can help: the active compounds in the herb are anti-proliferative.
A 2014 review published in Oncotarget found that cannabinoids inhibited cell proliferation in breast, prostate, and lung cancers. These anti-proliferative effects are thought to apply to other cancers and medical conditions as well.
A year earlier, in 2013, a team of Italian scientists found that non-psychoactive CBD protected against cancer cell “migration, adhesion, and invasion”.
Back in 2010, researchers found that cannabis also had an anti-proliferative effect in deep infiltrating endometriosis, where painful lesions appear on various female reproductive organs. Endometriosis increases your risk of developing cancer.
2. Anti-metastatic
When cancer cells migrate from part of the body to another, the cells become metastatic.
Cancer cells break away from the original tumor, travel through the blood or lymph system, and make a home elsewhere in the body. This is why some people with breast cancer later develop cancers of the bone, liver, brain, or lungs.
Recent research discovered that cannabinoids block metastasis. Over the past two decades, Spanish scientists at the Complutense University of Madrid have been studying the impact of cannabinoids and cancer cells.
In 2012, they found that compounds in the herb had anti-metastatic effects in tumor cells. In a recent review, lead author Guillermo Velasco cited over 12 studies evidencing cannabinoid protection against metastatic cancers.
3. Anti-angiogenesis
For tumors to survive, they need blood. Unfortunately, they take all of the blood they need through a process called angiogenesis. This enables tumors to grow blood vessels, and helps them grow larger and larger over time until they impede normal bodily function.
Researchers have been trying to develop drugs which stop tumors from creating blood cells. Fortunately, cannabinoids seem to do just that.
In 2008, a Spanish research team led by Cristina Blázquez discovered that psychoactive THC weakens a tumor’s ability to develop new blood vessels. While the team looked at brain cancer cells called gliomas specifically, they mention that the same effects have been found in melanomas and skin carcinomas as well.
Additional research from 2011 from Vanderbilt University cited evidence that non-psychoactive CBD is also anti-angiogenic, though it works differently from THC. This is big news, as it shows that the active compounds in cannabis fight tumor cells in a variety of ways.
4. Apoptosis
Already, cannabinoids stop tumor cells from spreading, slow down growth, and cut off their blood supply. But, can cannabis actually kill cancer cells? Research suggests that it can.
A recent study published in Current Oncology found that both THC and CBD were effective in killing neuroblastoma cells. Neuroblastomas are the most common tumors among children. With this particular type of cancer, CBD was more effective.
But, how? Simply said, CBD caused the brain tumor cells to commit suicide. The technical name for cell suicide is apoptosis. Apoptosis is a natural mechanism that the body uses to clear out cells that are damaged and ineffective.
This phenomenon is known as “programmed cell death” and it helps maintain the health of your cells. For some reason, cancer cells no longer die. They evade apoptosis. Research as early as 1998 has found that cannabinoids like CBD (cannabidiol) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) trigger apoptosis in tumor cells, meaning they actually die.
NOAGENATION.COM
