SmartBioScience
#GERD#Hyperglycemia#LIPH#Fasting#HyaluronicAcid #Collagen #LiverGallbladderCleanse #Hemp #Stress #BrainAge #Drugs #EndocrineDisruptiors #Hypertension#Microplastics #WaterSmarts #ToxicChemicals #LiverHealth #MilkThrisle #Magnesium #LiverCleanse #MedicinalMushroomsForAtheleticPerformance #BrainBoostingMedicinalMushrooms #RoyalColloids #CalciumDGlucarate #ProteinMalfunction #MedicinalMushrooms #JapaneseLongevitySecret #PlantarFasciitis #BlackCuminTheBlackGold #ThroatThyroidEsophagusLarynx#BasicBiohacks#SkinHealth#VariousLipids #Radiation #LungHealth #Sinkholes #Praying #HepatitisC #ImmuneBoostingFoods #ImmuneBoostingSupplements #ImmuneBoostingBiohacks #BetaGlucans #BetaGlucanKids #Phytoplankton
Top 7 Collagen Benefits
1. Improves Health of Skin and Hair
As we age, collagen production declines — it’s happening as you read this! You’ll notice it physically: looser skin, more wrinkles and less elasticity. Increasing collagen levels can help your skin look firmer, increase smoothness, and help your skin cells keep renewing and repairing normally.
Double-blind, placebo-controlled studies investigating the anti-aging properties of collagen have found that 2.5–5 grams of collagen hydrolysate used among women aged 35–55 once daily for eight weeks significantly improved skin elasticity, skin moisture, transepidermal water loss (dryness) and skin roughness, all with little to no side effects. (1) This makes collagen one of the best natural skin care ingredients available.
Collagen also reduces cellulite and stretch marks. When skin loses its elasticity as a result of decreased collagen, there’s another side effect: more visible cellulite. Because your skin is now thinner, cellulite becomes more evident — no more hiding what’s happening below the surface. Improving your skin’s elasticity through collagen helps reduce that dimpling on your skin.
Even severe stages of EDS (Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome) are completely cured with Collagen.
2. Reduces Joint Pains and Degeneration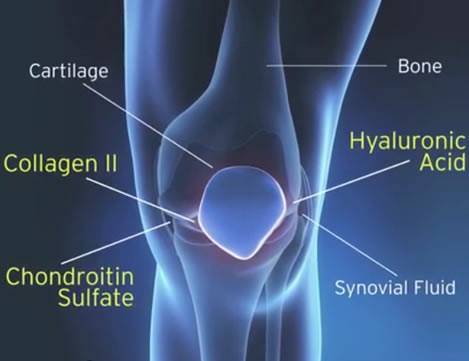
Have you ever felt like you’ve got “skeleton legs,” the types that feel extra stiff and cause pain when you move? Yup, that’s likely a loss of collagen rearing its ugly head. That’s because when we lose collagen, our tendons and ligaments start moving with less ease, leading to stiffness, swollen joints and more.
With its gel-like, smooth structure that covers and holds our bones together, collagen allows us to glide and move without pain. Think of ingesting more collagen like greasing a creaky door hinge: It helps your joints move more easily, reduces pain often associated with aging and even reduces the risk of joint deterioration. It’s no surprise then that a recent study even found that collagen is an effective treatment for treating osteoarthritis and other joint pain and disorders.
Researchers at Harvard’s Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston found that supplementing with type 2 collagen helped patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis find relief from painful symptoms by decreasing swelling in tender joints. Another study published in the International Journal of Medical Sciences found that people with osteoarthritis joint pain treated with type 2 collagen show significant enhancements in daily activities, such as walking up stairs, ascending or sleeping, and a general improvement in their quality of life.
If you suffer from leaky gut syndrome, a condition where bad-for-you toxins are able to pass through your digestive tract, collagen can be super-helpful. It helps break down proteins and soothes your gut’s lining, healing damaged cell walls and infusing it with healing amino acids.
The biggest digestive benefit of consuming more collagen is that it helps form connective tissue and therefore “seals and heals” the protective lining of the gastrointestinal tract. Today, we know that many illnesses can actually be traced back to inflammation or irritation stemming from an unhealthy gut. Poor gut health — including changes in the gut microbiome and permeability in the gut lining — allows particles to pass into the bloodstream where they can kick off an inflammatory cascade (hence the name leaky gut syndrome).
Studies have found that in patents with inflammatory bowel disease, serum concentrations of collagen are decreased. Because the amino acids in collagen build the tissue that lines the colon and GI tract, supplementing with collagen can help treat gastrointestinal symptoms and disorders, including leaky gut syndrome, IBS, acid reflux, Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. In addition to helping heal leaky gut, collagen also helps with the absorption of water within the intestines, keeping things moving more freely out of body.
4. Boosts Metabolism, Muscle Mass and Energy Output
A boost in collagen may help increase your metabolism by adding lean muscle mass to your frame and helping with the conversion of essential nutrients. One of glycine’s most important roles is helping form muscle tissue by converting glucose into energy that feeds muscle cells. And remember that retaining muscle mass is crucial as you age, since it helps support posture, bone health and burns more calories than fat. When consuming collagen, you can benefit from also consuming vitamin C to ensure your body can convert the collagen into a useable protein. This can begin to restore the source or your energy and vitality.
That’s not all that glycine can do for your metabolism. Research shows glycine also has important roles in both functions of the digestive and central nervous systems, which play big roles in maintaining a healthy, youthful body. Glycine seems to help slow the effects of aging by improving the body’s use of antioxidants and is also used in the process of constructing healthy cells from DNA and RNA.
In addition, it’s been found that arginine boosts the body’s ability to make protein from other amino acids, which is important for repairing muscle tissue, healing wounds, sparing tissue wasting, boosting the metabolism, and aiding in proper growth and development. And glutamine also helps maintain adequate energy by facilitating the synthesizing of many chemicals. This amino acid provides “fuel” to our cells, including carbon and nitrogen.
5. Strengthens Nails, Hair and Teeth
Ever had peeling and splitting nails? Well, a lack of collagen could be to blame. Collagen protein is the building block of your fingernails, hair and teeth. Adding collagen into your diet regimen can help keep your nails strong and possibly reverse signs of hair loss.
A study published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology found that there’s an “essential relationships between extracellular matrix (ECM) and hair follicle regeneration, suggesting that collagen could be a potential therapeutic target for hair loss and other skin-related diseases.”
6. Improves Liver Health
If you’re looking to detox your body of harmful substances, improve blood flow and keep your heart young, collagen is extremely helpful. That’s because glycine helps minimize damage your liver experiences when it absorbs foreign substances, toxins or alcohol that shouldn’t be passing through it.
One of the easiest ways to cleanse your liver is with a bone broth fast, but my favourite is the 1 Day Gallbladder/Liver Cleanse. Doctors often recommend a three-day bone broth detox to rapidly repair leaky gut. Vegan variation to it is using Agar Agar. This may help your body rid itself of chemicals and “reset” your gut, improving overall immune function. Studies have even found that glycine can be used to help reduce alcohol-induced liver damage and other forms of acute or chronic liver injury.
7. Protects Cardiovascular Health
The amino acid proline helps your artery walls release fat buildup in the bloodstream, shrinking the fat in the arteries and minimizing fat accumulation. Proline is needed for tissue repair within the joints and arteries, plus it helps control blood pressure. As part of collagen found within joints, it buffers our bodies from the effects of vibration or shock and helps us hold on to valuable cartilage as we get older. It’s also linked with the prevention of arteriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) since it helps our arteries stay clear of dangerous plaque buildup.
In addition, arginine helps with nitric oxide production, which allows for better vasodilation — meaning the widening of arteries and relaxation of muscle cells and blood vessels that allows for better circulation.
What Is Collagen? Types and Sources
A little known fact is that there are at least 16 different types of collagen within the human body. These include collagen types 1, 2, 3, 5 and 10. However, the vast majority of the collagen — between 80 percent and 90 percent — consists of types 1, 2, and 3. Type 1 collagen specifically accounts for almost 90 percent of the body’s supply according to some findings. There are also different types of collagen found in certain foods or used to create collagen products and supplements.
- Type 1: This is by far the most abundant, and almost considered to be the strongest, type of collagen found in the human body. It’s made up of eosinophilic fibers that form parts of the body, including tendons, ligaments, organs and skin (dermis). Type 1 collagen also helps form bones and can be found within the GI tract. It’s very important for wound healing, giving skin its stretchy and elastic quality, and holding together tissue so it doesn’t tear.
- Type 2: Type 2 collagen primarily helps build cartilage, which is found in connective tissues. The health of our joints relies on cartilage made of type 2 collagen, which is why it’s beneficial for preventing age-associated joint pain or various arthritis symptoms.
- Type 3: Type 3 collagen is made of reticular fibers and a major component of the extracellular matrix that makes up our organs and skin. It’s usually found with type 1 and helps give skin its elasticity and firmness. It also forms blood vessels and tissue within the heart. For these reasons, deficiency in type 3 collagen has been linked to a higher risk for ruptured blood vessels and even early death, according to results from certain animal studies.
- Type 4: Type 4 collagen has the important job of forming basal lamina, which is found in endothelial cells that form tissue that surround organs, muscles and fat. Basal lamina are needed for various nerve and blood vessel functions. They line the majority of our digestive organs and respiratory surfaces. Basal lamina can be found in the spaces between the top layer of skin/tissue and the deepest layer. They’re a thin layer of gel-like fluid that provides cushion/padding for the tissue above it.
- Type 5: This type of collagen is needed to make the surface of cells, as well as hair strands and tissue found in women’s placentas (the organ that develops in the uterus during pregnancy, provides oxygen and nutrients to the growing baby, and removes waste).
- Type 10: Type 10 helps with new bone formation and forming articular cartilage. It’s involved in the process of endochondral ossification, which is how bone tissue is created in mammals. It’s been found to be beneficial for bone fracture healing and repairing of synovial joints.
NOAGENATION.COM

